Gravity Casting Manufacturer
- Our gravity casting service provides high-strength, low-porosity components with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Ideal for aluminum and brass alloys, it supports complex geometries, perfect for automotive, aerospace, and industrial parts requiring durability, precision, and cost-effective production.
- Dimensional Accuracy: ±0.3mm–1.0 mm
- Surface finish: Ra 3.2 µm
- Tooling cost is 30–60% lower than HPDC
- Supports complex designs with thin walls and undercuts
Common Steps of Gravity Casting
Each casting follows a precise series of steps to ensure quality, consistency, and durability in every gravity-cast component.
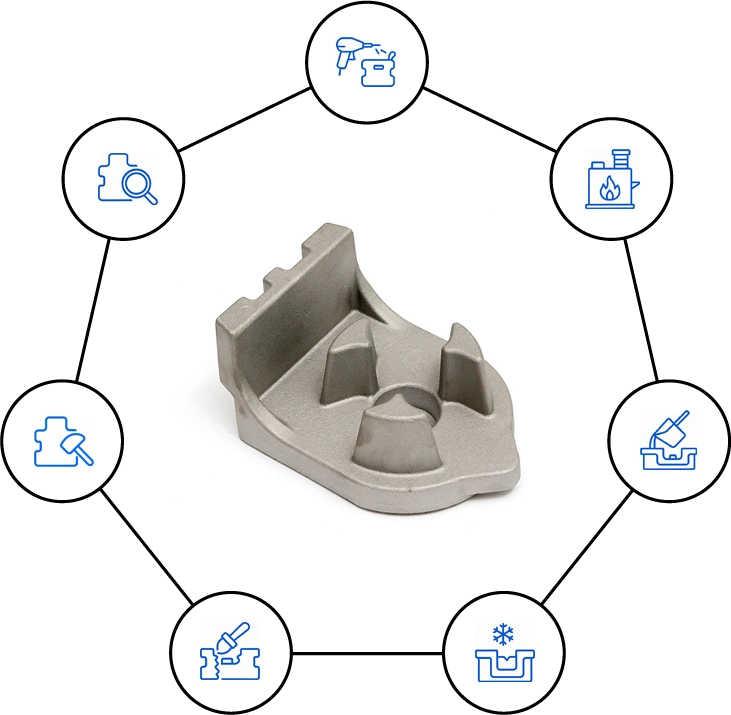
Mold Preparation
Prepare sand or metal molds by cleaning, preheating, and applying a suitable coating for smooth metal flow.
Melting the Metal
Heat the chosen metal alloy in a controlled furnace until it reaches the required pouring temperature for casting.
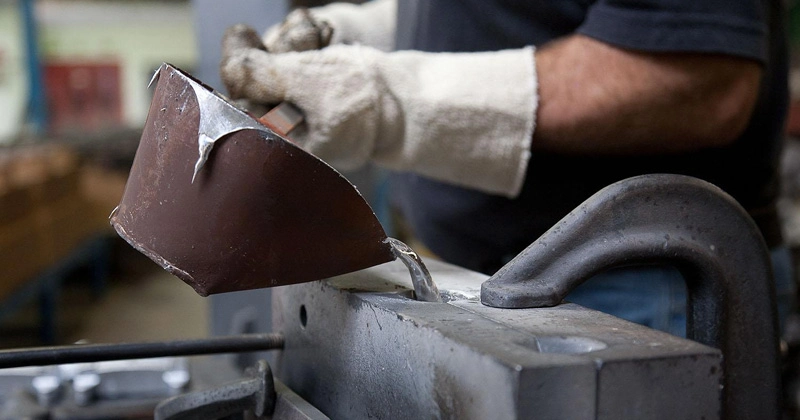
Pouring the Molten Metal
Pour molten metal steadily into the mold cavity using gravity without external pressure to ensure complete filling.
Cooling and Solidification
Allow the molten metal to cool and solidify naturally inside the mold, forming the desired casting shape.
Mold Removal
Break or open the mold carefully to retrieve the solidified casting without damaging the finished component surface.
Finishing and Cleaning
Trim, deburr, and clean the casting to remove excess material and improve surface finish and dimensional precision.
Inspection and Quality Control
Perform dimensional checks and defect inspections to ensure the casting meets specifications and required industry standards.
Main Die Casting Process Types
Our die casting encompasses several process types, each tailored to specific materials, part designs, and production needs. Below are the most common types:

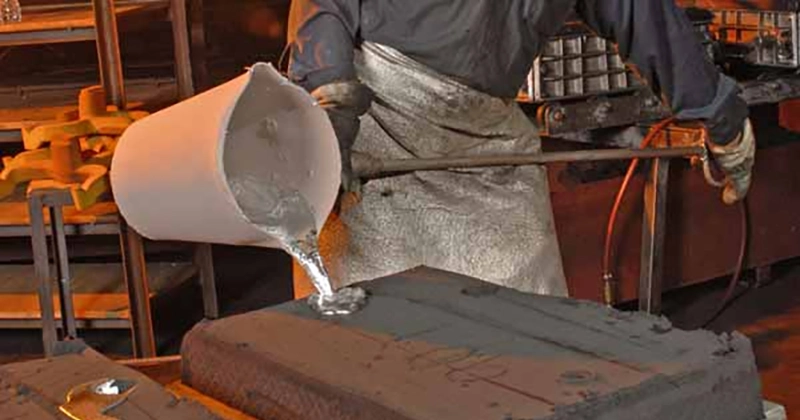
Gravity Die Casting
- Uses permanent metal molds for improved accuracy and smoother surface finish.
- Suitable for aluminum or brass parts with strength and minimal porosity.
- Mold preheating and precise pouring reduce shrinkage and enhance casting quality.

Sand Casting
- Employs single-use sand molds for intricate shapes and large-scale castings.
- Ideal for low-volume production with flexible, low-cost tooling options.
- Involves manual or automated mold forming, pouring, cooling, and mold removal.
Available Metal Materials
We offer high-performance die casting alloys, including aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper (brass, bronze), lead, tin, and occasionally ferrous alloys for special uses.

Ferrous Metals
- Cast iron offers strength, wear resistance, and excellent vibration-damping properties.
- Cast steel provides toughness, weldability, and durability for heavy structural components.
- Carbon steel delivers good strength, machinability, and affordability for general engineering use.
- Alloy steel enhances hardness, heat resistance, and strength for critical mechanical applications.

Nonferrous Metals
- Aluminum alloy is corrosion-resistant, lightweight, and used in automotive, aerospace industries.
- Copper alloy offers great conductivity, resists corrosion, and is utilized in electrical components.
- Zinc alloy enables fine, precise casting for small, decorative or functional parts.
- Magnesium alloy features high strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for lightweight structural applications.
Tolerance for Die Casting Services
We follow industry-standard tolerances to ensure precision, though actual values vary by geometry, alloy, tooling, and casting size. Typical ranges include:
| Tolerance Parameter | Typical Range | Notes |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.3 mm to ±1.0 mm | Depends on part size, mold quality, and alloy used |
| Wall Thickness | ±0.5 mm to ±1.5 mm | Thicker walls improve dimensional stability |
| Flatness | ±0.3 mm to ±1.0 mm | May vary with part size and cooling rate |
| Straightness | ±0.2 mm per 100 mm | Affected by solidification shrinkage and mold design |
| Roundness | ±0.2 mm to ±0.8 mm | Applicable to circular and cylindrical features |
| Hole Diameter | ±0.3 mm to ±1.0 mm | Influenced by core material and casting complexity |
| Surface Finish (Ra) | Ra 3.2 µm to Ra 12.5 µm | Based on mold material and coating technique |
| Angular Tolerance | ±0.5° to ±1.5° | Depends on mold alignment and part complexity |
| Bore Tolerance | ±0.4 mm to ±1.2 mm | Secondary machining recommended for tight fits |
| Draft Angle | 1° to 3° | Required for easy removal from the mold |
| Shrinkage Allowance | 1.0% to 1.5% | Varies by alloy and geometry |
| Coating Thickness | ±0.02 mm to ±0.05 mm | Applies to painted, anodized, or plated surfaces |
Inspection Techniques
We uphold strict quality control through a combination of precise inspection techniques that ensure dimensional accuracy, surface integrity, and internal soundness of every casting.
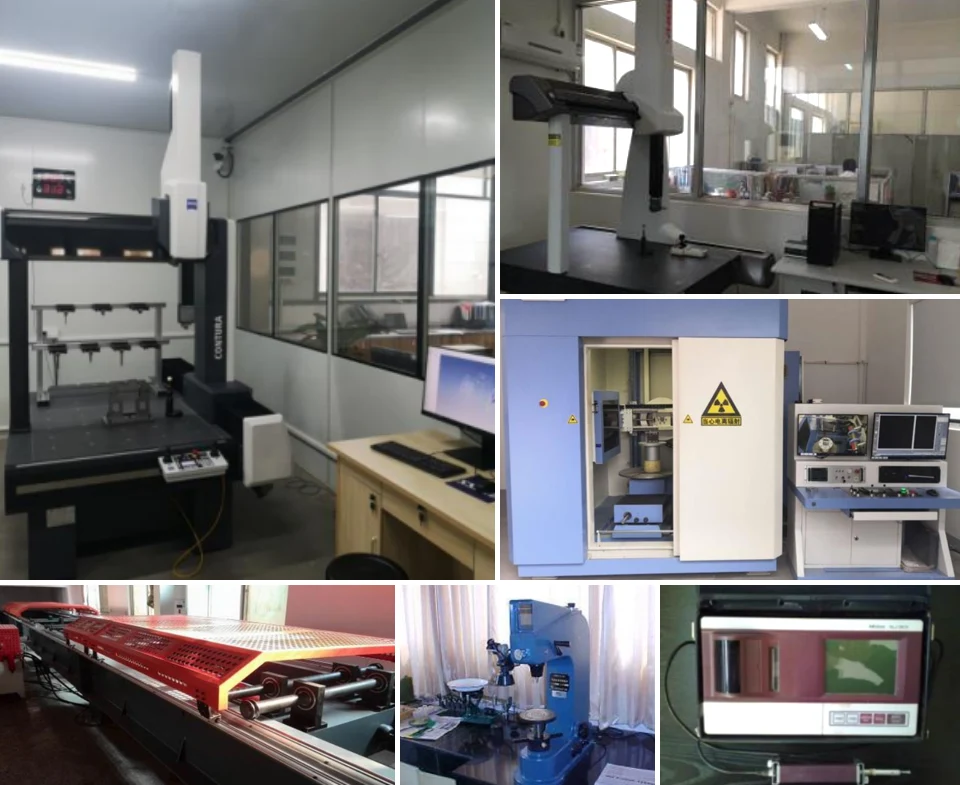

Visual Inspection
Inspectors examine castings for visible defects like cracks, porosity, cold shuts, and misruns under proper lighting and magnification tools.
Dimensional Inspection
We use calipers, micrometers, and CMMs to ensure all dimensions meet specified tolerances, typically within ±0.3 mm to ±1.0 mm.
Surface Roughness Measurement
Surface finish is tested using roughness testers. Polished molds typically achieve Ra values ranging from 3.2 µm to 12.5 µm.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Dye penetrant, ultrasonic, and X-ray testing detect internal and surface defects without damaging the integrity of the casting.
Hardness Testing
We conduct Brinell or Rockwell hardness tests to evaluate material strength, wear resistance, and compliance with mechanical property requirements.
Metallographic Examination
Prepared samples are microscopically examined to assess grain structure, porosity levels, and alloy uniformity in gravity-cast metal components.
Pressure and Leak Testing (If Applicable)
Castings for fluid applications undergo pressurized air or hydraulic tests to confirm structural integrity and leak-free sealing performance.
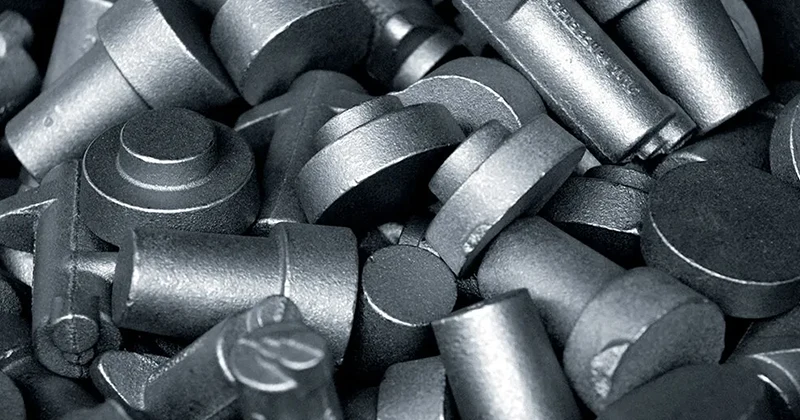
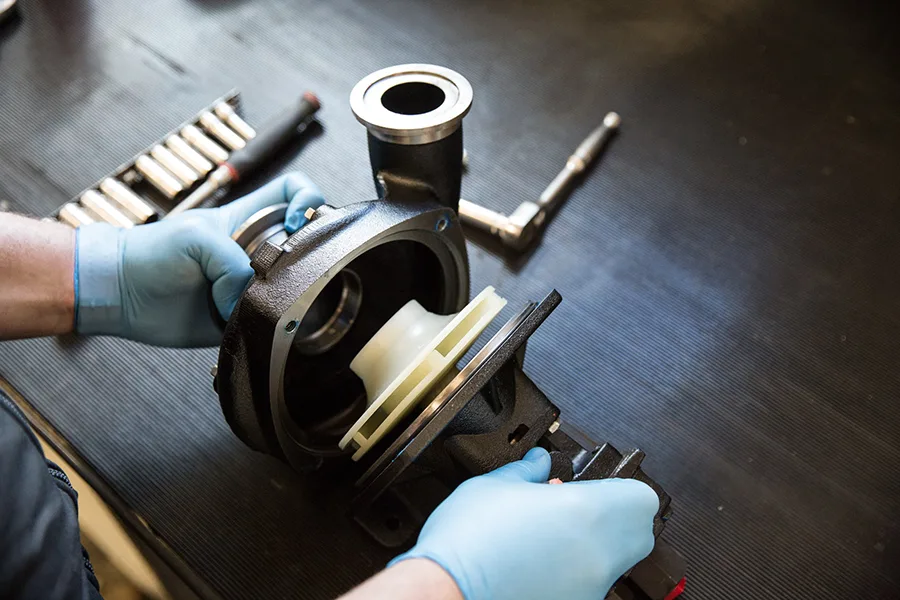
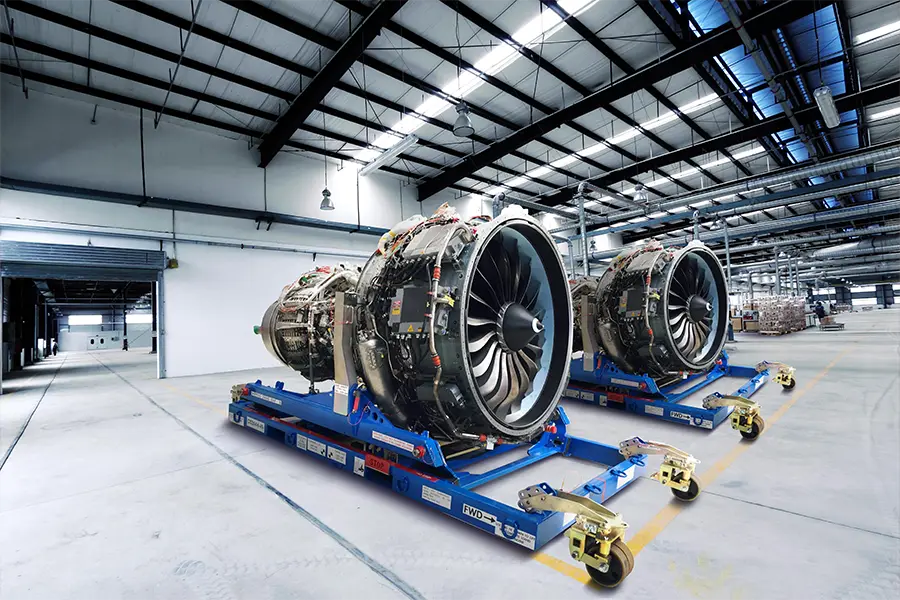
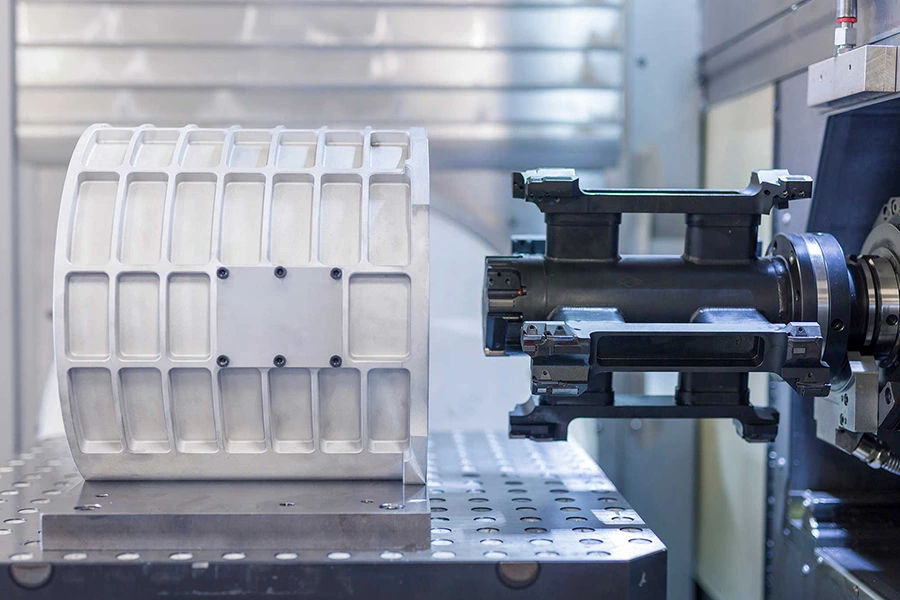
Our Gravity Casting Parts
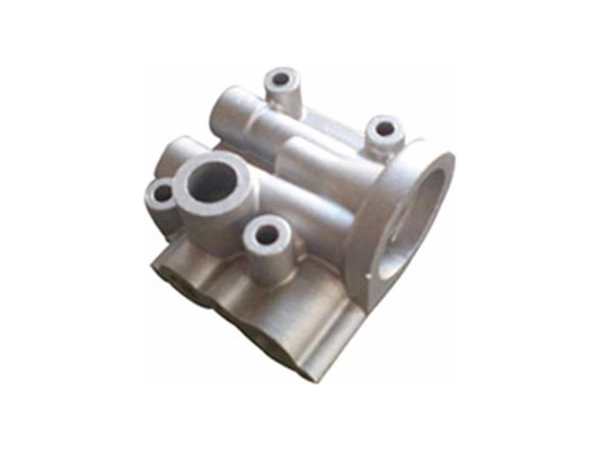
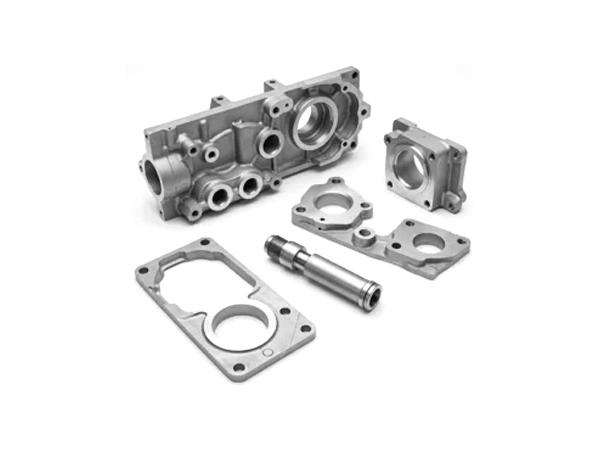
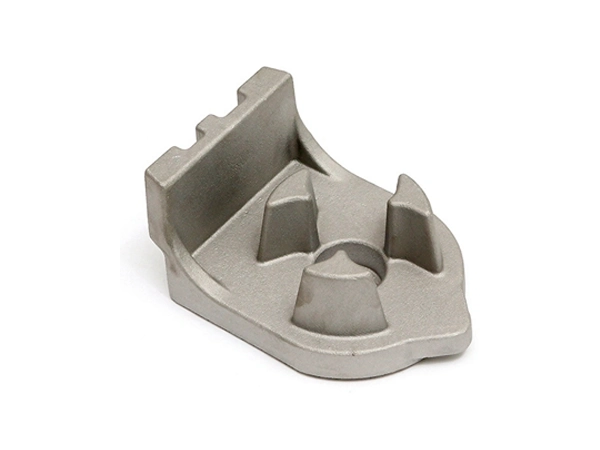
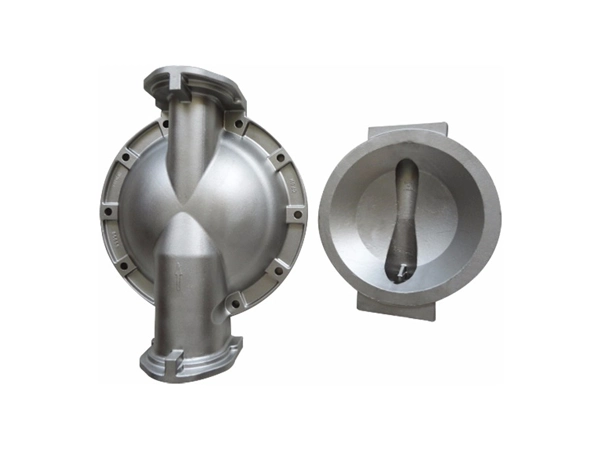
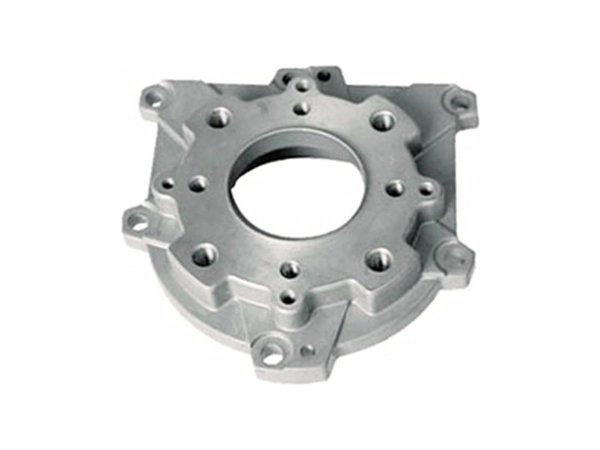
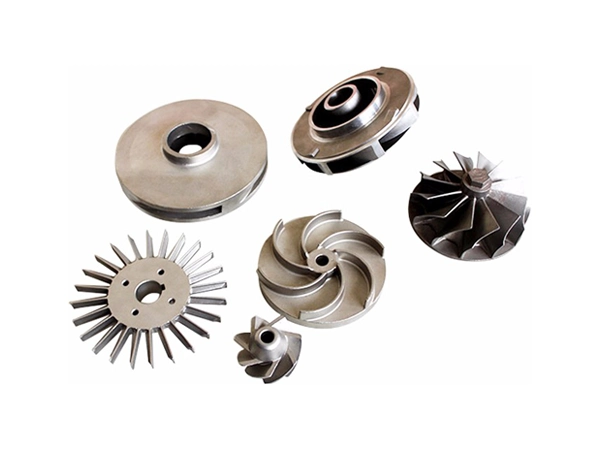






Applications
Our gravity casting services are widely applied across industries that demand strong, precision-cast metal parts with excellent dimensional stability. Typical application areas include:
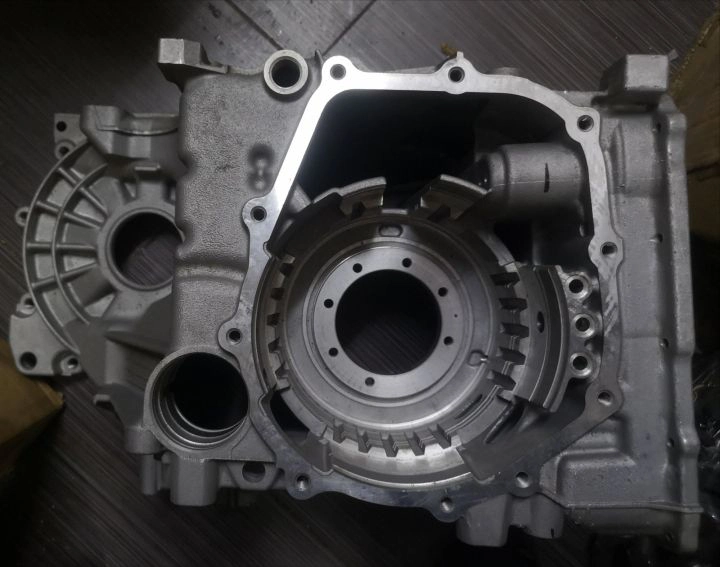

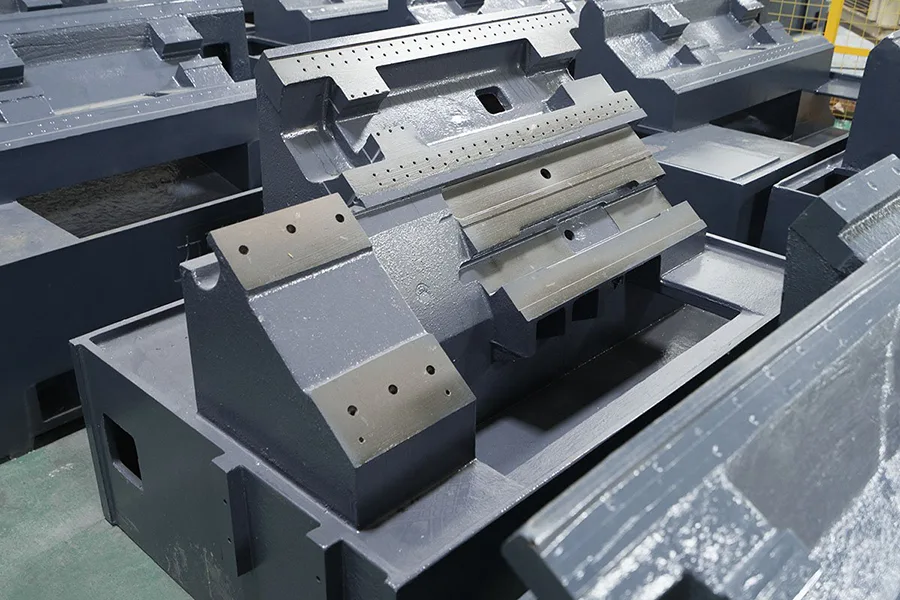


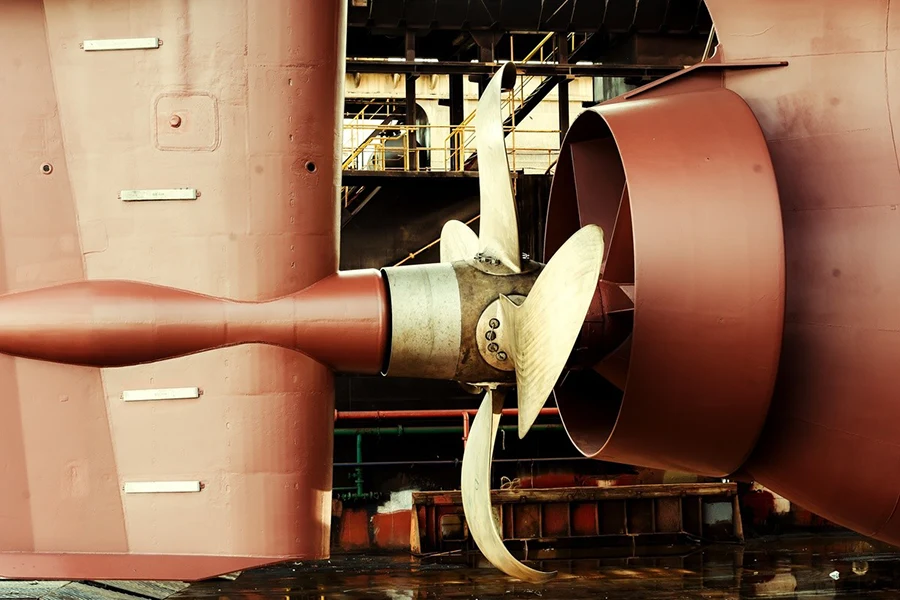
🚗 Automotive Industry
Production of engine components, gearbox housings, brackets, oil pump covers, and transmission parts requiring strength, accuracy, and durability.
💨 Pumps & Valves
Manufacture of impellers, volutes, valve bodies, and pump housings where corrosion resistance and smooth internal surfaces are critical.
🛠 Industrial Equipment
Casting of machine bases, structural supports, motor housings, and custom mechanical parts for heavy-duty applications.
✈ Aerospace & Defense
Fabrication of non-critical structural parts, enclosures, and hardware that require weight reduction without sacrificing integrity.
💡 Electrical & Power Systems
Components such as motor brackets, enclosures, heat sinks, and insulator mounts used in electrical transmission and control systems.
🌊 Marine Applications
Corrosion-resistant castings for propeller hubs, water pump parts, and structural brackets used in harsh saltwater environments.
Contact Us Now
FAQs
Do you provide 3D modeling support?
Yes, we accept and assist with CAD files (STEP, IGES, etc.) for mold and part development.
Is gravity casting suitable for complex parts?
Yes, it supports moderate complexity, including cores and undercuts, though extreme complexity might require other methods like investment casting.
What part sizes can you produce?
We cast small to medium parts, typically ranging from 50 grams up to 30 kilograms depending on mold and alloy.
What post-processing do you offer?
Services include trimming, shot blasting, CNC machining, heat treatment, and surface coating per customer requirements.
What testing do you provide?
We offer dimensional inspection, visual checks, X-ray, dye penetrant, and mechanical testing as required for quality assurance.
How does gravity casting differ from die casting?
Gravity casting relies on gravity, not pressure, offering lower tooling costs and fewer defects, but slightly slower cycle times than die casting.