Custom Die Casting Services
- We deliver precision die casting solutions with high output, tight tolerances, and smooth surface finishes.
- Our efficient, high-speed processes minimize machining, shorten lead times, and deliver complex, cost-effective parts tailored to diverse industries and custom specifications.
- ±0.1 mm Dimensional Accuracy
- Thin Walls Down to 0.75 Mm
- Casts Complex Shapes with Sleeves and Inserts
- Tensile Strength Reaches 415 MPa
- Cuts Finishing Time by 60%
- Reduces Cost by 25–45% in High Volumes
Common Steps of Die Casting
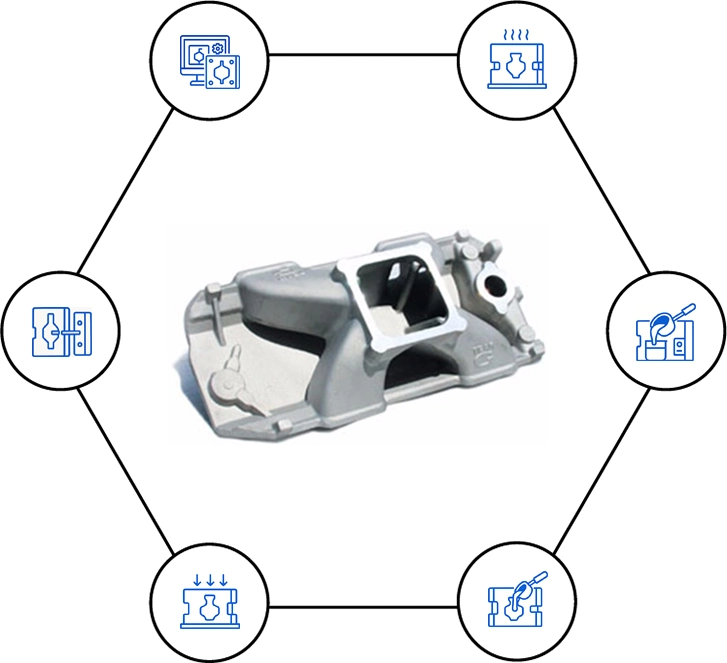
Design and Mold Creation
Mold Heating
Metal Melting
Injection of Molten Metal
Cooling and Solidification
Mold Opening and Part Removal
Main Die Casting Process Types
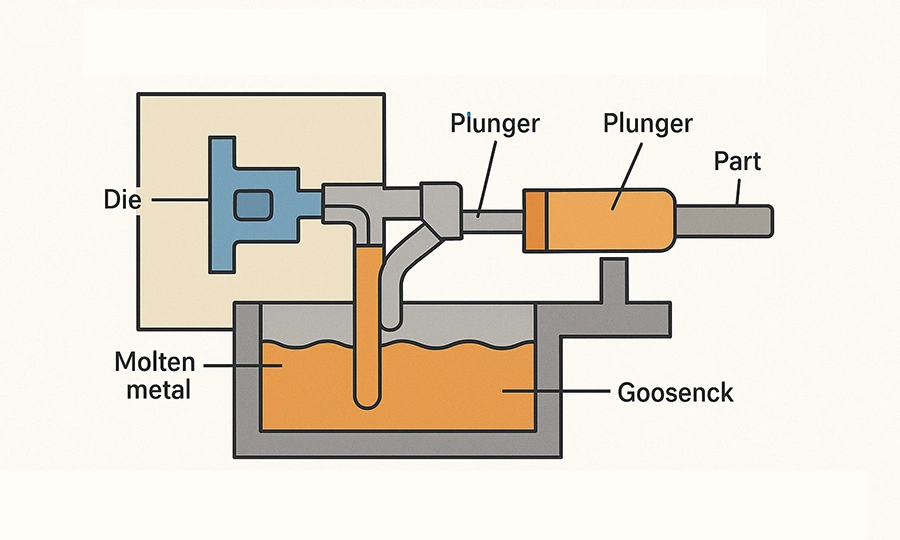
Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Injection system is submerged in molten metal for faster, continuous cycles.
- Suitable for low melting point metals like tin, zinc, and lead.
- Enables short cycle times and low cost for small to medium parts.
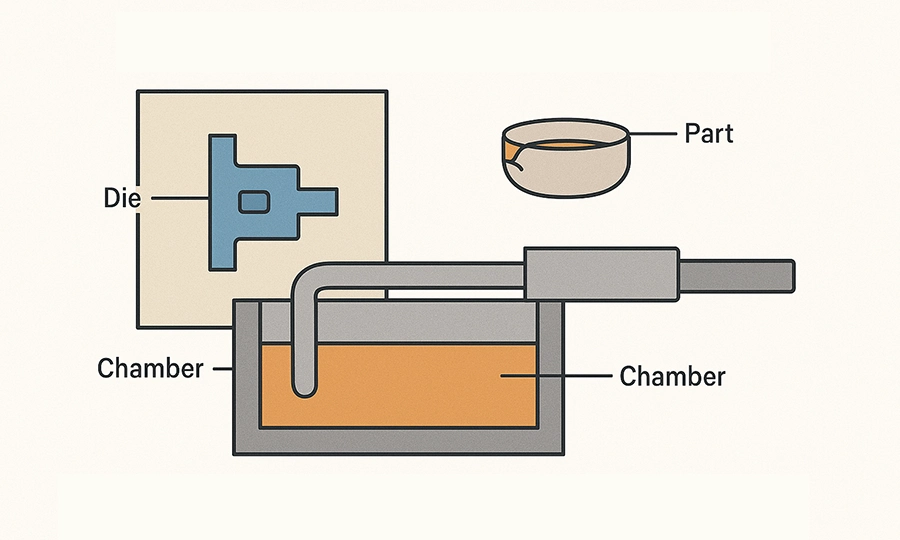
Cold Chamber Die Casting
- Ladled molten metal is injected into a different chamber.
- Ideal for aluminum, brass, and copper with high melting points.
- Casts larger, stronger, and more complex parts with precision.
Available Metal Materials

Aluminum Alloys
- Model: A319, A356, A380, A383, ADC6, ADC12, A360
- Corrosion-resistant and Lightweight; ideal for automotive, aerospace, and industrial use.
- Great for thin, complex parts with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.
- Recyclable, economical, and supports anodizing, painting, and powder coating.

Zinc Alloys
- Model: Zamak2, ZA12, ZA27, Zamak3, Zamak5, Zamak7, ZA8.
- Best for small, precise parts like locks, gears, and enclosures.
- Strong, corrosion-resistant, and provides excellent plating surface.
- Low melting point extends die life and reduces machining needs.

Magnesium Alloys
- Model: AZ31B, AE42, EZ33, AZ91D, AM60B, AM50A, AS41.
- Applied in automotive, aerospace, and electronics for light structures.
- Simple machining and quick solidification for intricate pieces.
- Offers EMI shielding and heat control for electronics.
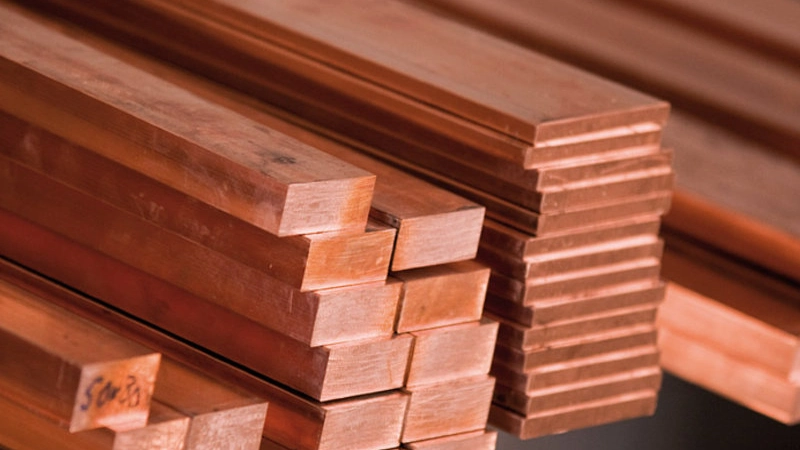

Copper Alloys
- Model: C83600, C84400, C87300, C87500, C87850, C86200, C83800.
- Ideal for plumbing, marine, and electrical precision parts.
- Offers high strength, pressure resistance, extreme environment durability.
- Easily casts details, supports multiple finishing treatments.
Surface Treatment
To improve the appearance, performance, and durability of die cast parts, we offer various surface treatments based on material, use, and finish needs.
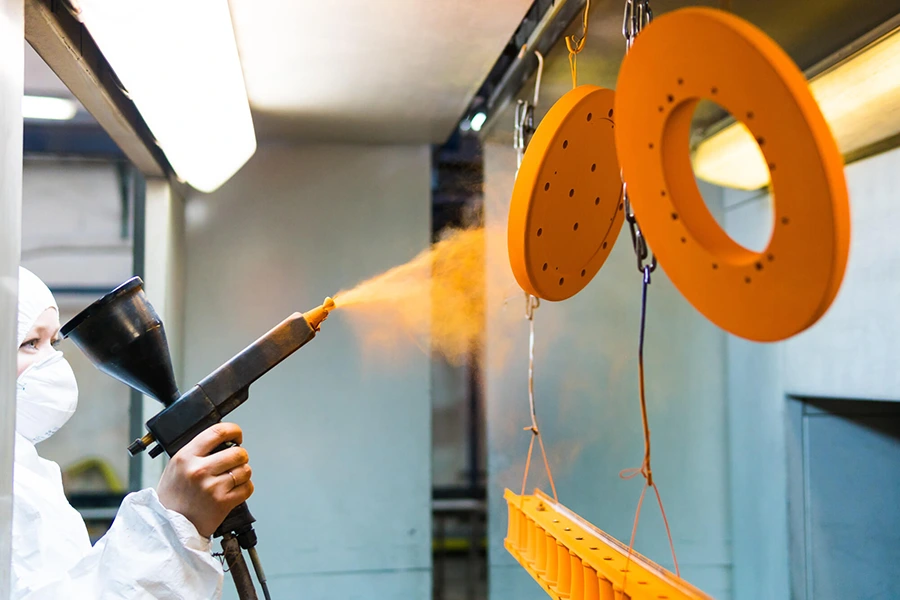








Hot-dip Galvanizing
Zinc Plating
Chrome Plating
Spray Painting
Powder Painting
Polishing
Anodizing
Black Oxide
Dimensions in Die Casting
Accurate dimensional control is essential in die casting to ensure part quality, function, and compatibility with assemblies. Below are key dimensional considerations:
| Parameter | Specification |
| Maximum Part Size | Up to 1,500 mm |
| Wall Thickness | 0.5 – 10 mm |
| Draft Angle | 0.5° – 3° per side |
| Tolerances | ±0.025 – ±0.2 mm |
| Fillet Radius | 0.5 – 5 mm |
| Parting Line Offset | Up to 0.3 mm |
| Hole Diameter | 1 – 50 mm |
| Aspect Ratio | Up to 10:1 |
| Surface Roughness | Ra 0.8 – 3.2 µm |
| Shrinkage Allowance | 0.5% – 1.2% |
Tolerance for Die Casting Services
We follow industry-standard tolerances to ensure precision, though actual values vary by geometry, alloy, tooling, and casting size. Typical ranges include:
| Tolerance Parameter | Typical Range | Notes |
| Dimensional Accuracy | ±0.05 mm to ±0.3 mm | Depends on part size, geometry, and die precision |
| Wall Thickness | ±0.1 mm to ±0.25 mm | Thin sections may increase variation due to metal flow |
| Straightness | ±0.1 mm per 100 mm | Affected by cooling rate and part length |
| Flatness | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm | Larger flat areas may require post-processing |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.4 to Ra 2.0 µm | Depends on mold surface and alloy type |
| Roundness | ±0.05 mm to ±0.25 mm | Applies to cylinders, holes, and bosses |
| Angular Tolerance | ±0.1° to ±1° | Related to die alignment and feature size |
| Hole Diameter | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm | Influenced by core pin stability and cooling |
| Core Pull Tolerance | ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm | Affected by core pull mechanism precision |
| Draft Angle | ±0.25° to ±1° | Required to release parts from mold |
| Thread Depth | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Tolerance tighter with post-machined threads |
| Bore Tolerance | ±0.1 mm to ±0.25 mm | Applies to internal cylindrical surfaces |
| Concentricity | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm | Measured between bores and outer profiles |
| Tapered Features | ±0.5° to ±1° | Supports easy mold ejection |
| Radii & Fillet Sizes | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm | Tool radius and cooling rate dependent |
| Perpendicularity | ±0.2 mm per 100 mm | Maintained through precise mold alignment |
| Material Homogeneity | ±0.5% | Refers to consistency in alloy composition |
| Shrinkage Rate | ±0.2% to ±0.5% | Influenced by alloy and cooling dynamics |
| Deflection | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | May occur in long, thin-walled castings |
| Casting Distortion | ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm | Varies with mold temperature and part complexity |
| Coating Thickness | ±0.01 mm to ±0.05 mm | For painted, plated, or anodized surfaces |
| Gap Tolerance | ±0.05 mm to ±0.3 mm | For moving parts or sliding assemblies |
| Bead and Seam Quality | ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm | Impacts assembly fit and surface appearance |
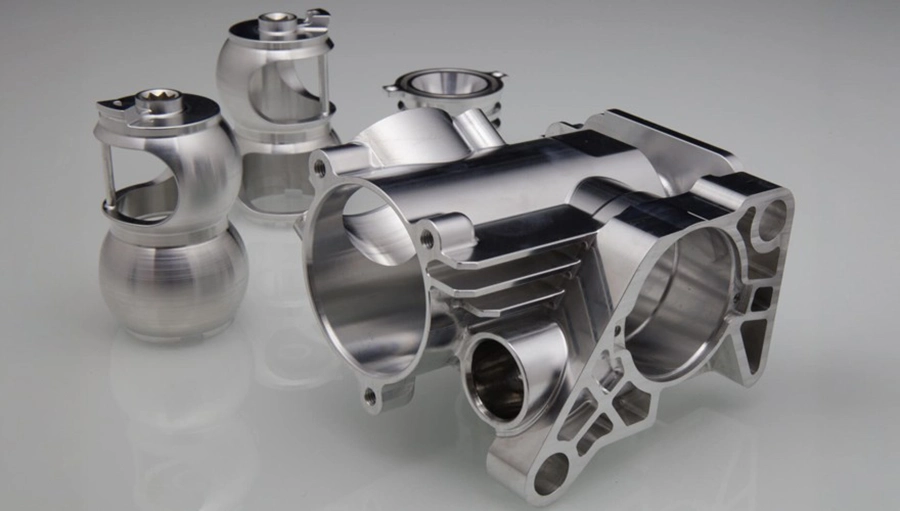
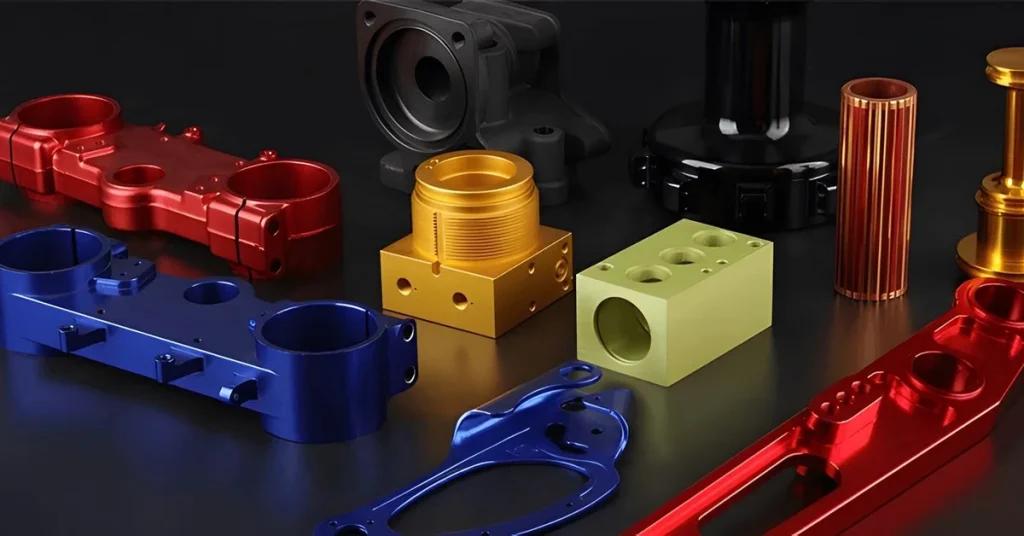
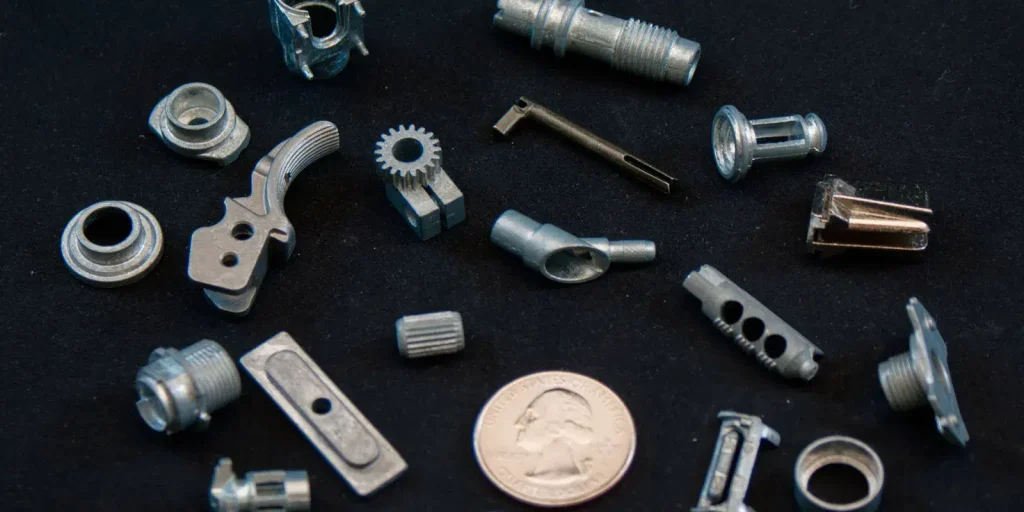
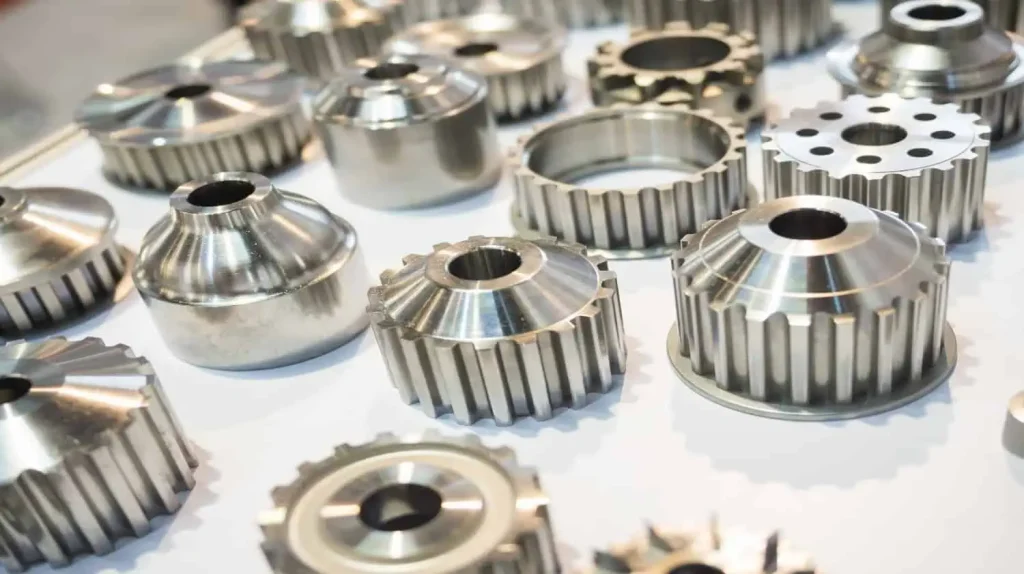
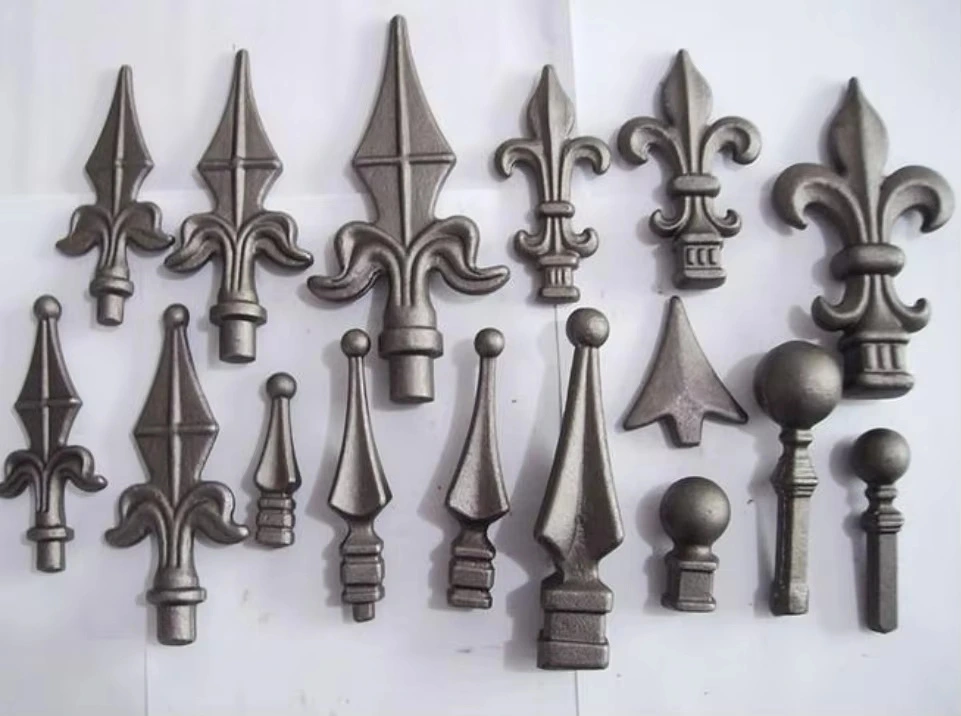
Our Die Casting Parts
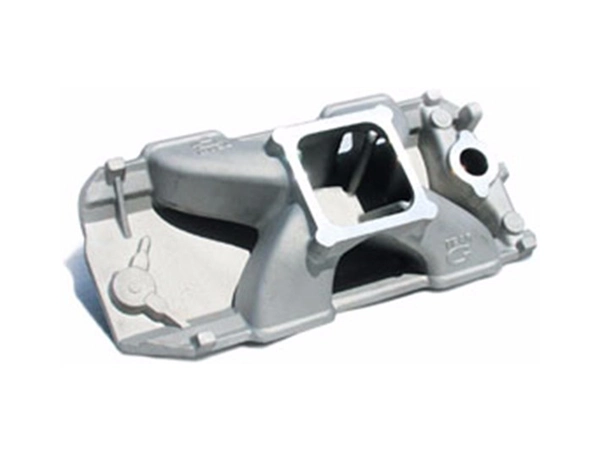
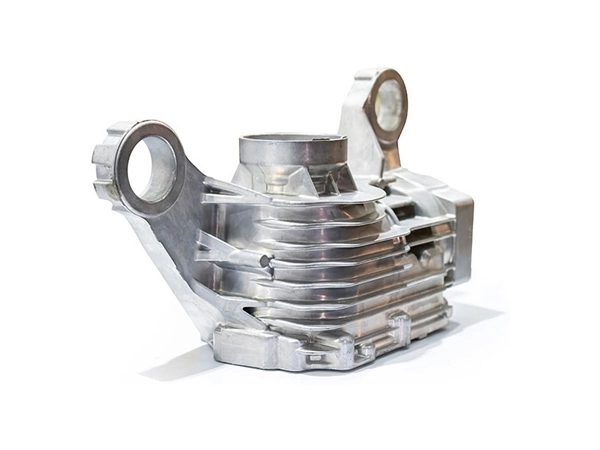
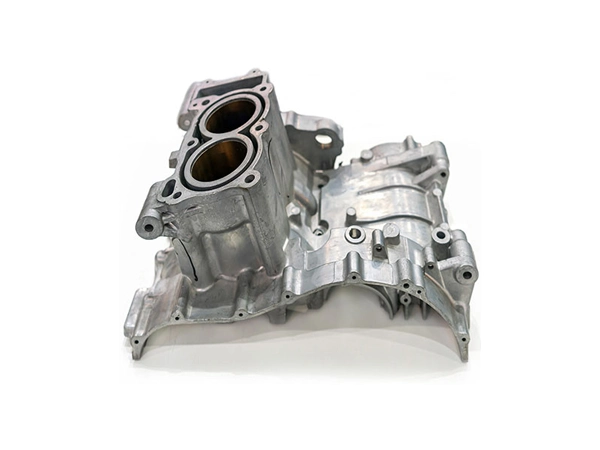
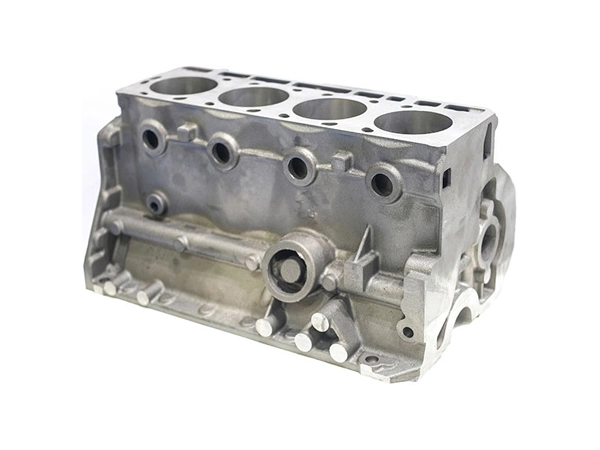
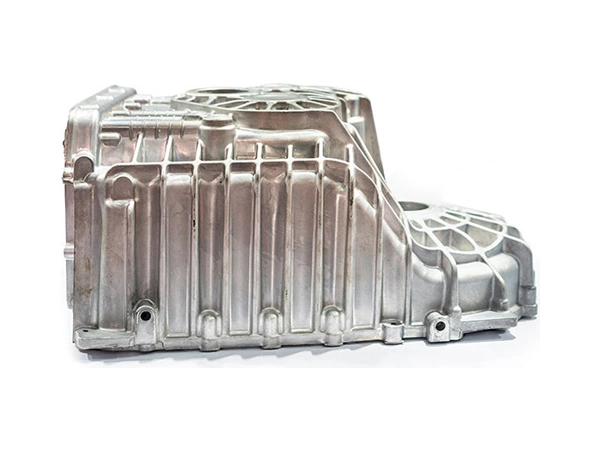
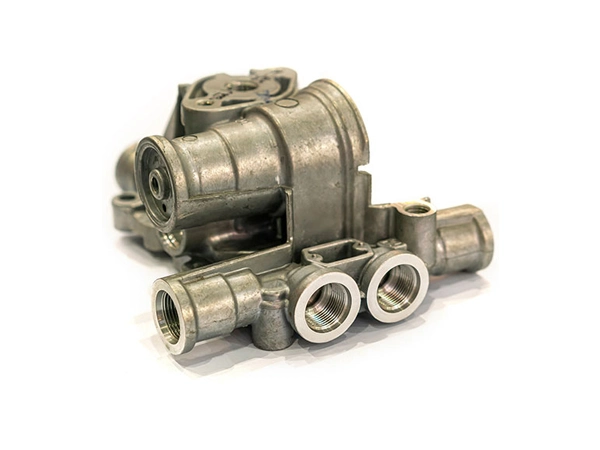






Applications
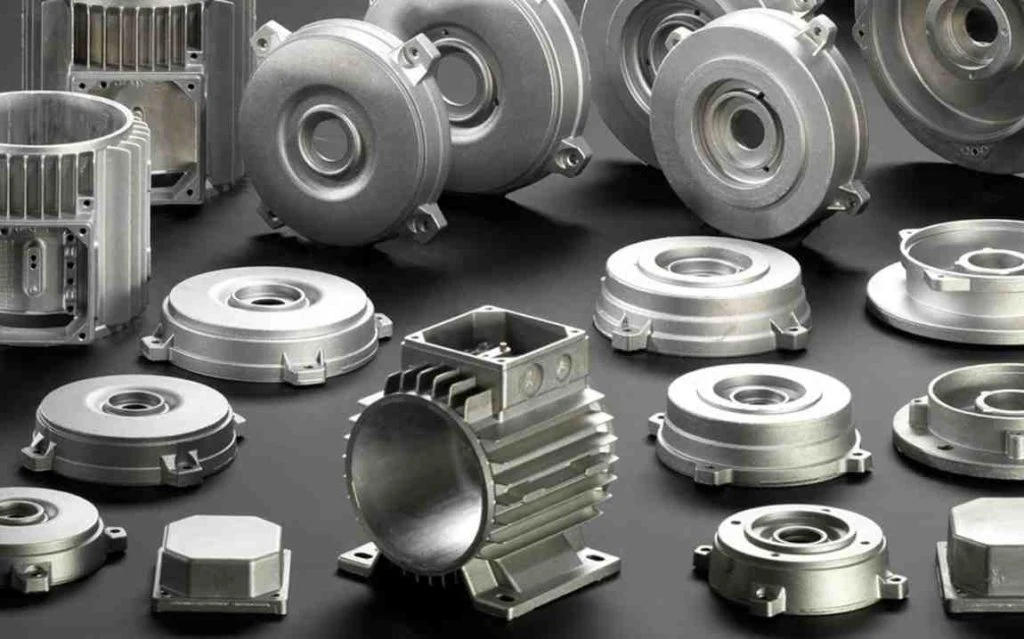
Our die casting solutions are widely utilized across diverse industries due to their precision, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Key application areas include:
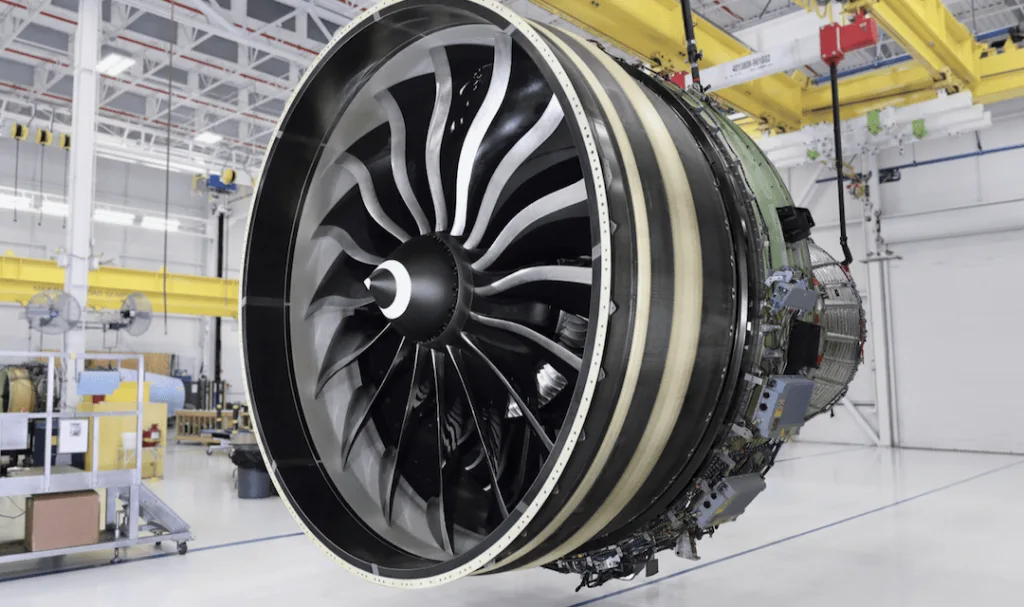

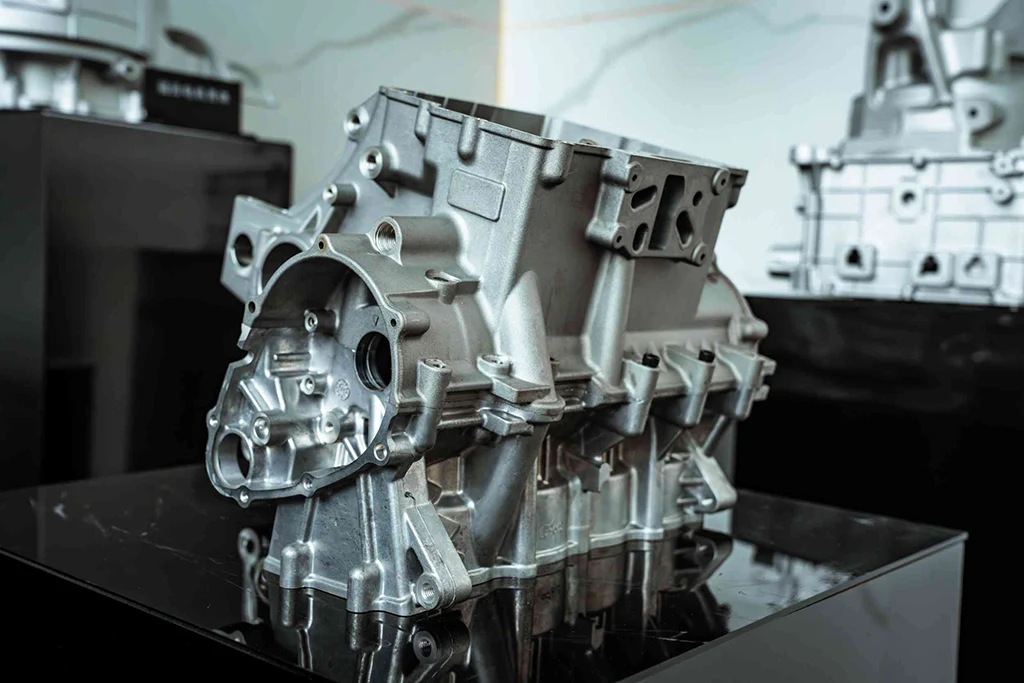





Aerospace
Automotive
Engine & Powertrain Components
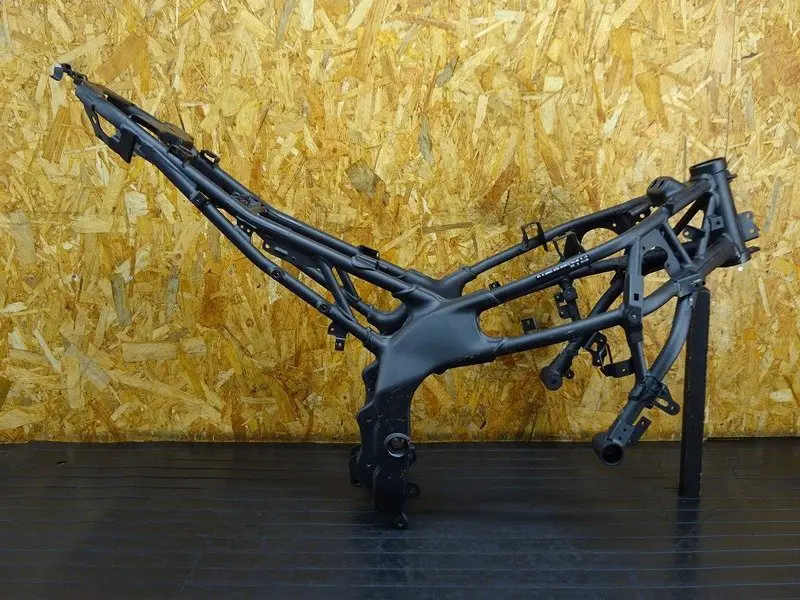
Motorcycle and Motor Manufacturing
Applied in the manufacturing of motorcycle frames, crankcases, and various motor housings, combining strength with lightweight performance.