Closed-die Forging Services
- Our closed-die forging delivers high-strength, precision parts with superior grain flow, surface finish, and minimal waste.
- It’s perfect for complex, high-volume parts with tight tolerances and reliable performance in aerospace, automotive, and industrial fields.
- Suitable for Various Metal Materials
- Minimal or No Post-Machining Required
- Supports Complex Part Geometries
- Extended Die and Tool Lifespan
- Cost-efficient for High-volume Production
Our Closed-die Forging Process
Precision and strict control are at the core of our forging process, which starts with digital design and ends with rigorous quality inspections to ensure consistent, high-strength parts.
Design Phase
We use CAD models and simulations to design dies, optimize material flow, and prevent forging defects before production begins.
01
Die Manufacturing
In-house die manufacturing uses CNC machining and heat-treated tool steel to ensure accuracy, durability, and long-term forging reliability.
02
Material Preparation
Billets are chosen, cut, and heated to controlled forging temperatures, ensuring proper plasticity, grain flow, and structural consistency.
03
Forging Operation
Heated billets are pressed into shaped die cavities under high pressure to form parts with precise geometry and strength.
04
Trimming and Post-Processing
Flash is removed using trimming dies. Heat treatment, cleaning, or CNC finishing can be performed to meet part requirements.
05
Inspection and Quality Control
Finished parts undergo strict inspections, including dimensional checks, hardness tests, and NDT to ensure top-quality forged components.
06
Based on Forging Method
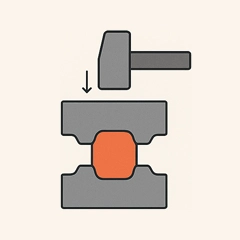
Closed-die Drop Forging
- Hammering deforms heated metal between dies for accurate shaping.
- Ideal for small-to-medium complex, high-strength parts.
- Ensures tight tolerances, good finish, and material efficiency.
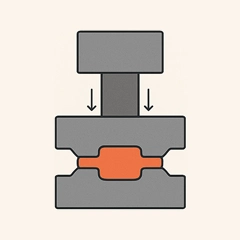
Closed-die Press Forging
- Hydraulic or mechanical presses apply steady force to shape metal.
- Ideal for large parts needing strong grain flow.
- Produces dense, low-flash parts with consistent structure.
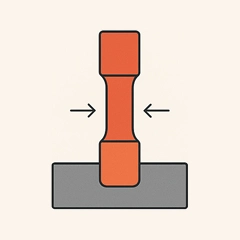
Closed-die Upset Forging
- Compresses metal axially to enlarge diameter at specific zones.
- Used for fasteners, shafts, and headed components.
- Enhances alignment, strength, and fatigue resistance.
Based on Flash Formation
Closed-die forging can be categorized by how excess material is handled during the forming process. The two main types are:
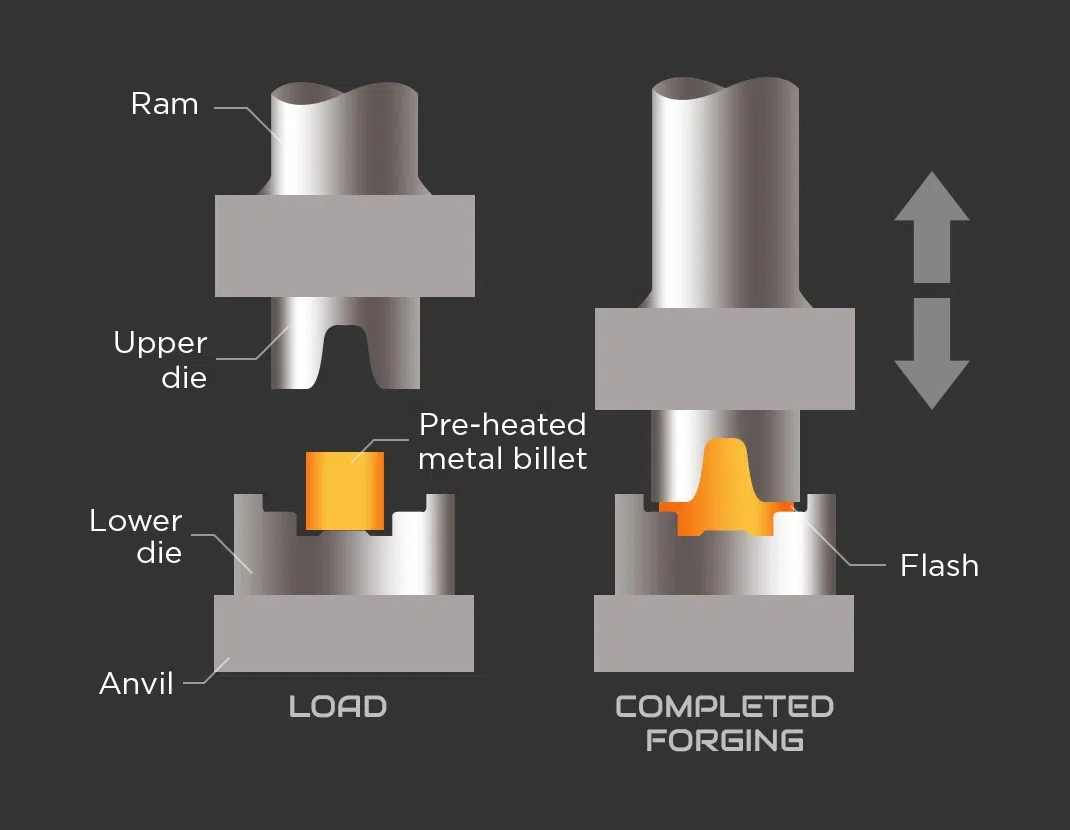
Closed-die Forging with Flash
This method forces excess metal into a surrounding cavity, enhancing material flow, die fill, and part strength while increasing material waste.
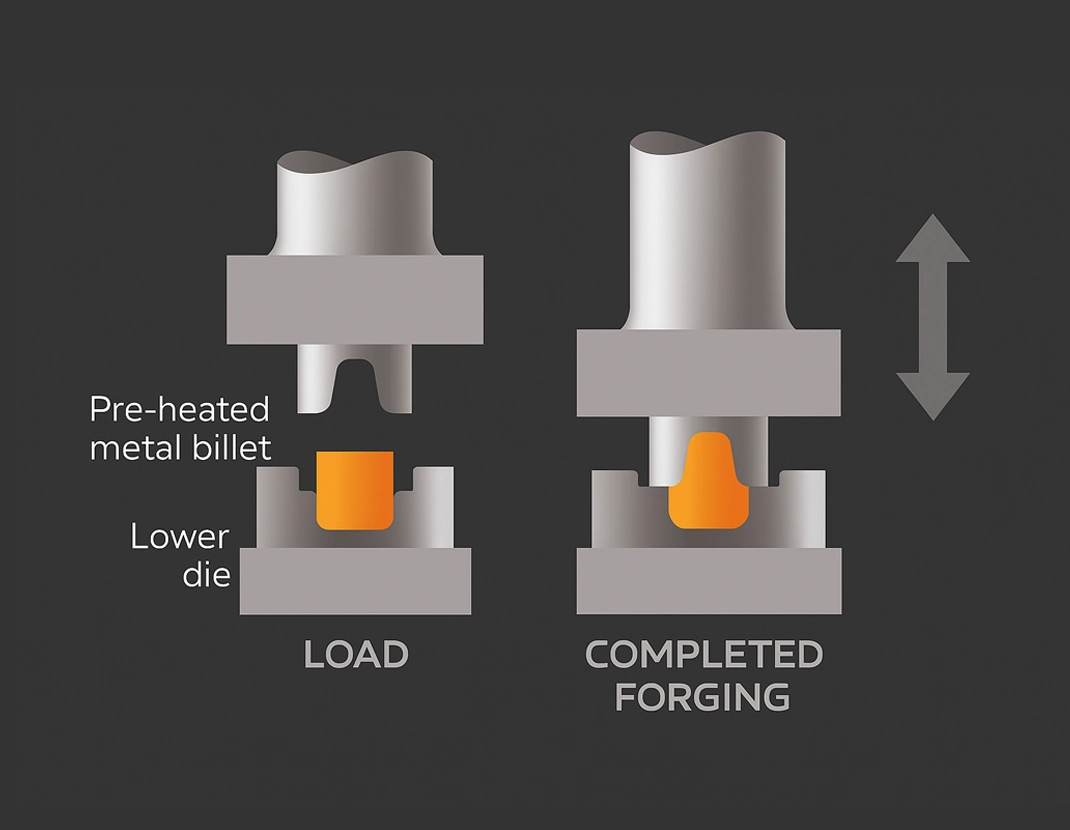
Closed-die Forging without Flash
Precisely confines metal within die cavities without overflow, reducing material loss and trimming needs, ideal for near-net shape and high-efficiency production.
Materials Used in Closed-die Forgings

Carbon Steel
Alloy Steel
Stainless Steel
Aluminum Alloys
Titanium Alloys
Nickel-Based Alloys
Brass and Copper
Tolerance for Closed-die Forging Services
We maintain tight tolerances across all closed-die forging operations to ensure superior part quality, structural integrity, and dimensional precision. Our standard tolerance ranges include:
| Parameter | Tolerance Range |
| Forging Grain Flow | ±10° to ±20° |
| Die Wear | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm |
| Carbon Content Uniformity | ±0.1% to ±0.3% |
| Tolerance of Critical Features | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm |
| Concentricity | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm |
| Temperature Uniformity | ±5°C to ±10°C |
| Thickness Variation | ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm |
| Angular Deviation | ±0.2° to ±0.5° |
| Distortion / Warpage | ±0.3% to ±0.5% |
| Burr Height | ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm |
| Parting Line Offset | ±0.2 mm to ±0.4 mm |
| Forging Finish Depth | Ra 0.4 µm to Ra 1.0 µm |
Closed-Die Forging Applications

Aerospace
Turbine discs, landing gear parts, structural brackets.
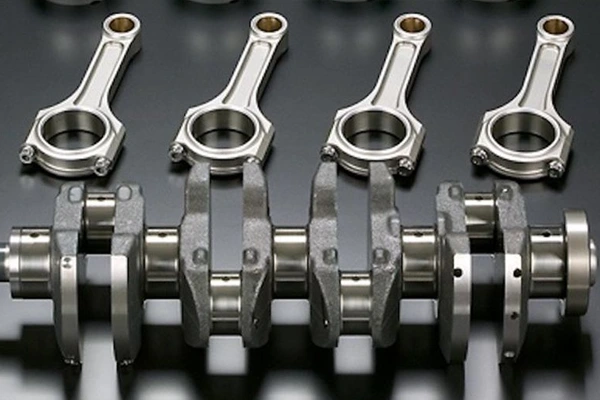

Automotive
Connecting rods, crankshafts, gear blanks, control arms, rocker arms, axle beams, axle shafts, idler arms, steering yokes.
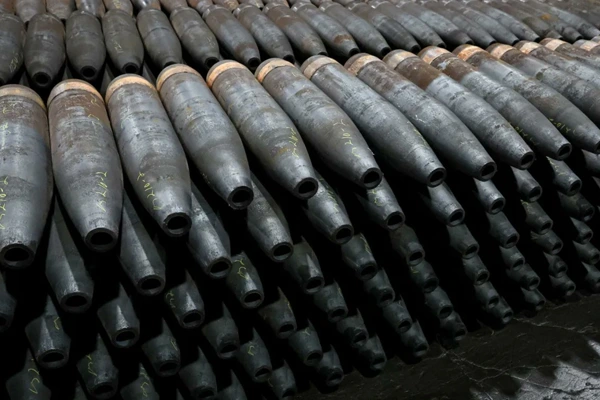

Defense
Missile casings, armored vehicle components.
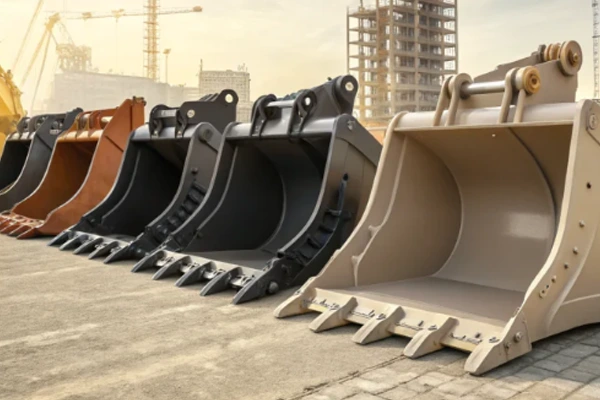

Industrial & Construction Machinery
Flanges, shafts, couplings, pump housings, excavator bucket teeth.
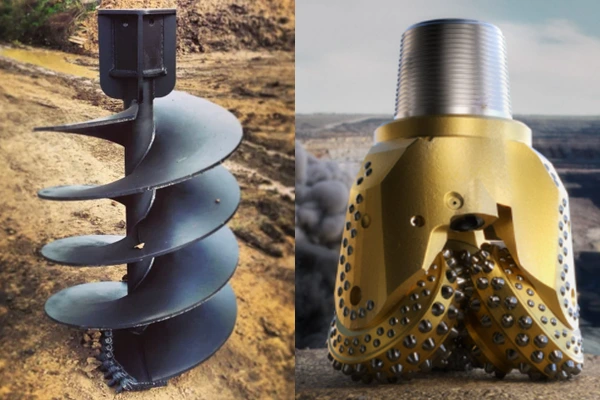
Mining Industry
Ground drilling bits, auger bits.
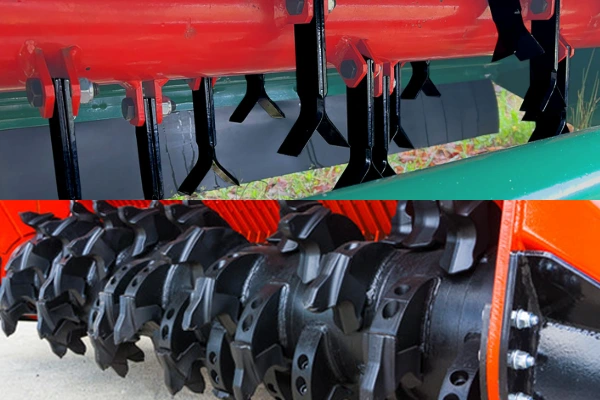

Forestry Equipment
Mulcher teeth, tub grinder teeth, flail hammer blades.
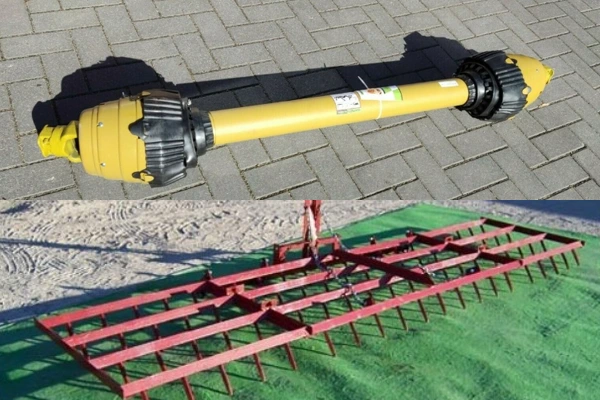

Agricultural Machinery
Drive shafts, gears, spike harrow teeth, tie rod ends.
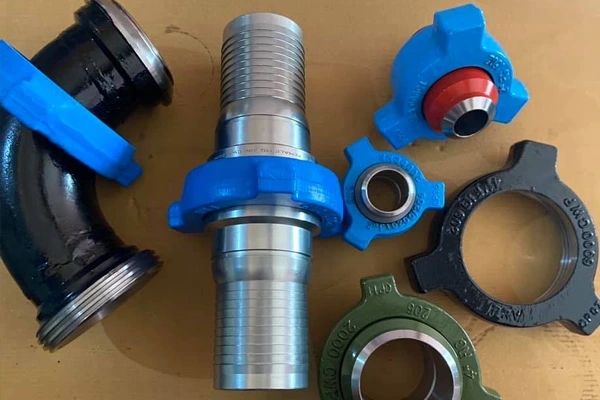

Oilfield Equipment
Elbows, hammer union nuts, tees, crosses.
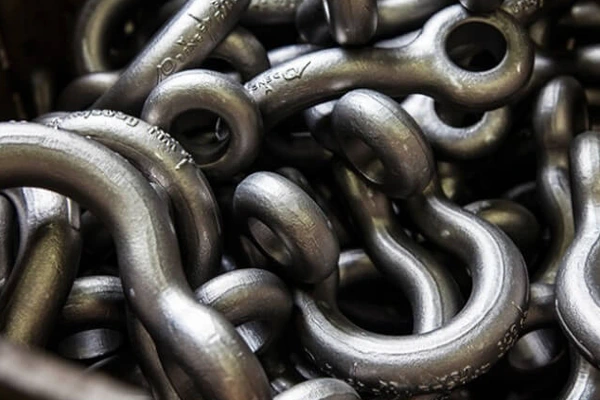

Lifting & Rigging
Shackles, weld-on D-rings, hooks.